
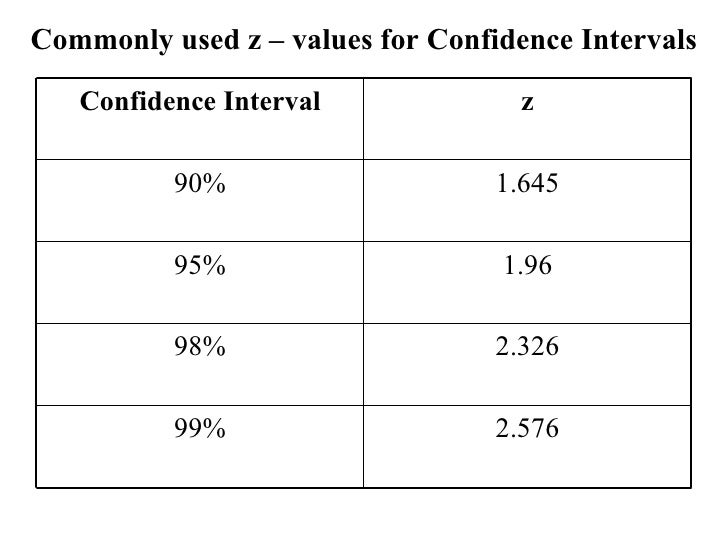
Let us consider the second case for which the given confidence level is 95. Of course, we don’t recommend waiting for 99% confidence either. Hence, the z value at the 90 percent confidence interval is 1.645. If you do one test a month, at least two likely had erroneous results. If you make ROI projections based on 80% confidence and roll out that experience, you have a one in five chance of missing them completely. Making decisions too early is one of the most common mistakes we see in A/B Testing. While there are a limited set of situations when this is okay, it is never ideal. In the digital community, it’s not uncommon to see A/B testing tools make calls at only 80% or 85% confidence. This is the standard confidence level in the scientific community, essentially stating that there is a one in twenty chance of an alpha error, or the chance that the observations in the experiment look different, but are not.Ĭommon Confidence Levels and Their Z-Score Equivalents The most commonly used confidence level is 95%. If you roll out this Variant Recipe, there is only a one in 20 chance that you will not see a lift.
If your two-sided test has a z-score of 1.96, you are 95% confident that that Variant Recipe is different than the Control Recipe. Z-scores are equated to confidence levels. What Does My Confidence Level Mean to Me in a Business Sense? We believe it’s just as important to know if your test is statistically underperforming as it is to know if it’s performing better than Control. If they establish the 99 confidence interval as being between 70 inches and 78 inches, they can expect 99 of 100 samples evaluated to contain a mean value. This means that there is a 99 probability that the true population parameter lies within the. With a one-sided test, you are only mathematically confident about one or the other, but never both. For a 99 confidence interval, the z-score is approximately 2.576. If you conduct a two-sided hypothesis test, you can be mathematically confident about whether or not your Variant Recipe is greater than or less than your Control Recipe. We use the Z-score calculator to test how far the center of the Variant bell curve is from the center of the Control bell curve. The Variant Recipe and all of the visitors in it make up a second bell curve.

In A/B Testing terms, all of your visitors are observations, and the Control experience makes up a bell curve. Digital Analytics Platform Implementationįrequently Asked Questions What is a Z-Score?Ī z-score is a standardized score that describes how many standard deviations an element is from the mean.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
